When it comes to managing your water system, choosing the right tank can make all the difference in performance and longevity. You might be wondering: should you go for a bladder tank or a pressure tank?
Both serve the important job of regulating water pressure, but they work in different ways and offer unique benefits. Understanding these differences is key to making a choice that fits your home’s needs and keeps your water flowing smoothly. You’ll discover exactly how bladder tanks and pressure tanks compare, what makes each one stand out, and which might be the better fit for your setup.
Keep reading to ensure your water system runs efficiently and lasts longer.
Credit: www.youtube.com
Bladder Tank Basics
Understanding bladder tanks is essential when comparing them to pressure tanks. These tanks play a key role in water systems. They help maintain steady water pressure and protect pumps from damage. Knowing their basics helps you make better choices for your needs.
Design And Construction
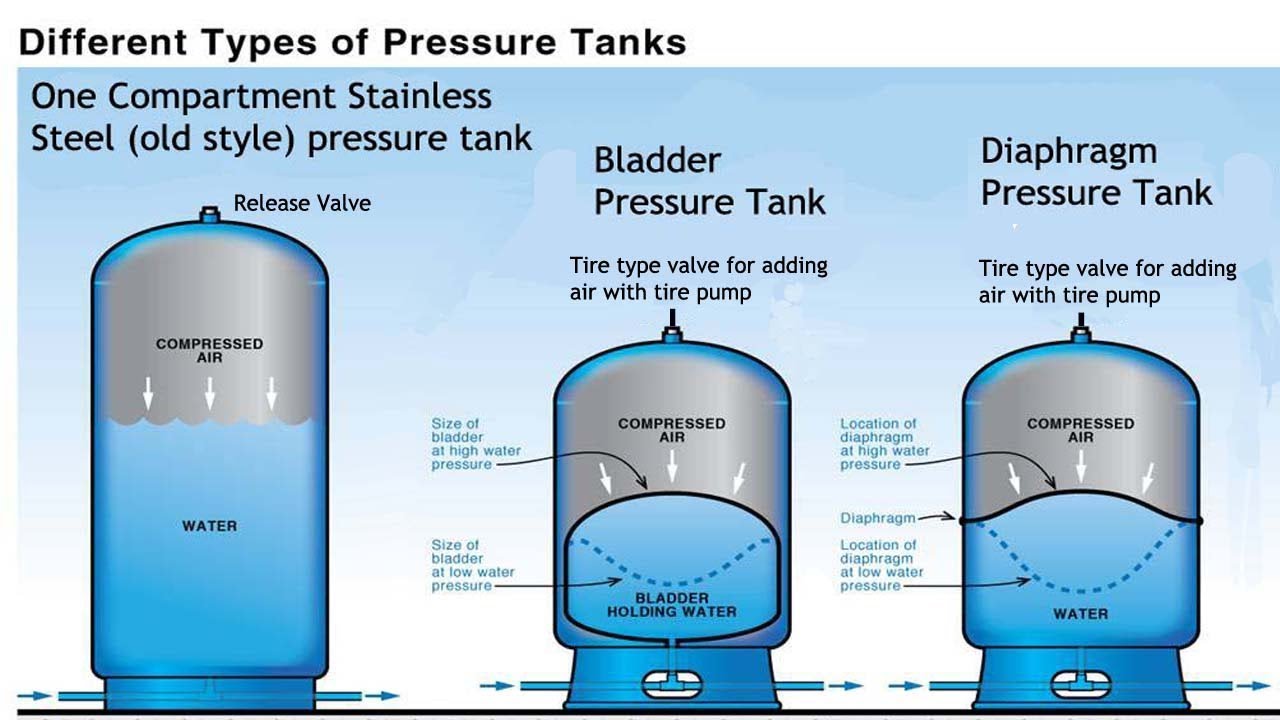
A bladder tank has a flexible rubber bladder inside a steel or composite shell. The bladder separates water from the air cushion. This design prevents air from mixing with water. The tank shell holds the bladder and keeps it secure. The bladder expands and contracts as water flows in and out.
How It Works
Water enters the bladder and pushes the bladder to expand. Compressed air outside the bladder creates pressure. This pressure pushes water out when a tap is opened. The bladder stops water from touching the tank walls. This reduces corrosion and keeps the system clean. It also limits pump cycling by storing water under pressure.
Common Uses
Bladder tanks are common in well water systems and booster pump setups. They help keep water pressure steady in homes and small businesses. These tanks protect pumps by reducing on-off cycling. They are also used in irrigation and rainwater collection systems. Their maintenance is simple since the bladder is sealed inside.
Pressure Tank Essentials
A pressure tank plays a key role in many water systems. It stores water and maintains pressure. This helps avoid frequent pump starts. A well-functioning pressure tank improves system life. It also ensures steady water flow for daily use.
Understanding pressure tanks is important when comparing bladder tanks versus pressure tanks. Knowing how pressure tanks work helps in making the right choice for your needs.
Structure And Materials
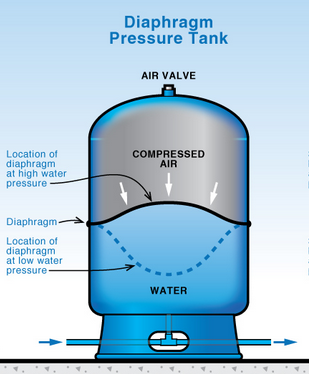
Pressure tanks usually have a steel or fiberglass shell. Inside, there is an air chamber or diaphragm. The air chamber stores compressed air. The diaphragm separates water from air in some models. This design prevents water from contacting the tank’s metal walls. It reduces rust and corrosion risks. Tanks come in different sizes to fit various systems.
Operating Principle
Pressure tanks use air pressure to push water out. When water fills the tank, it compresses the air inside. This creates pressure that forces water through pipes. The pump only runs when pressure drops below a set level. This cycle reduces pump wear and saves energy. It also prevents water hammer, which can damage pipes.
Typical Applications
Pressure tanks are common in well water systems. They help maintain constant water pressure. Many homes use them for drinking and irrigation water. Pressure tanks also work in booster pump systems. These tanks support water pressure in tall buildings or long pipe runs. They are essential in many industrial water setups too.
Performance Comparison
Choosing between a bladder tank and a pressure tank depends heavily on their performance. Both tanks store water and help maintain pressure in plumbing systems. Understanding how they differ in key performance areas helps make the right choice. This section compares water pressure consistency, pump cycling frequency, and durability factors.
Water Pressure Consistency
Bladder tanks keep water pressure steady by using a flexible bladder inside. The bladder separates air from water, reducing pressure drops. Pressure tanks use an air chamber to maintain pressure but may cause more fluctuations. This can lead to uneven water flow. Bladder tanks provide smoother pressure, ideal for sensitive appliances.
Pump Cycling Frequency
Bladder tanks reduce how often pumps turn on and off. The bladder allows more water storage before the pump activates. Pressure tanks often cause frequent pump cycling due to air mixing with water. Frequent cycling wears out the pump faster. Less cycling means longer pump life and energy savings with bladder tanks.
Durability Factors
Bladder tanks have a sealed bladder that prevents water from contacting the tank walls. This limits corrosion and extends tank life. Pressure tanks rely on air chambers that require regular maintenance to avoid waterlogging. A waterlogged tank can damage the pump and tank. Bladder tanks usually need less upkeep and last longer in tough conditions.
Maintenance Needs
Maintenance needs differ between bladder tanks and pressure tanks. Understanding these needs helps keep your system running smoothly. Proper care prevents breakdowns and extends tank life. This section explains key maintenance tasks for both tank types.
Routine Checks
Bladder tanks require less frequent checks. The internal bladder is sealed and mostly maintenance-free. Still, check air pressure yearly. Pressure tanks need regular air pressure checks too. Check the air charge with a pressure gauge. Look for leaks or waterlogged tanks. Inspect the tank exterior for rust or damage. Regular checks catch problems early.
Common Issues
Bladder tanks may lose air inside the bladder. This causes the bladder to over-expand and fail. Air loss also makes pumps cycle too often. Pressure tanks often face diaphragm wear or air loss. Waterlogging is common if the air chamber fails. Both tanks can suffer from corrosion or leaks. Spotting these issues early reduces repair costs.
Longevity And Repairs
Bladder tanks usually last longer due to the flexible bladder. Repairs often involve bladder replacement. Pressure tanks may need diaphragm replacement or air recharge. Rust can shorten tank life for both types. Keep tanks painted and dry to prevent rust. Routine maintenance extends tank lifespan. Timely repairs keep water pressure steady and pumps safe.
Cost And Value
Understanding the cost and value of bladder tanks and pressure tanks helps make smart choices. Both types serve well in water systems but differ in price and maintenance needs. We explore initial costs, long-term savings, and replacement factors to guide your decision.
Initial Investment
Bladder tanks usually cost more upfront than traditional pressure tanks. They include a rubber bladder inside that keeps water and air separate. This design adds to manufacturing costs. Pressure tanks are simpler and often cheaper to buy. The choice depends on your budget and system needs.
Long-term Savings
Bladder tanks reduce pump cycling by holding water under pressure efficiently. This lowers energy use and extends pump life. Pressure tanks may need more frequent maintenance, increasing costs over time. Fewer repairs and less energy use make bladder tanks more cost-effective in the long run.
Replacement Considerations
Bladder tanks have a bladder that can wear out and may need replacing. Replacement can be costly but happens less often with quality tanks. Pressure tanks need air checks and can corrode inside, leading to earlier replacement. Consider maintenance and lifespan when calculating total cost.

Credit: www.redriver.team
Suitability For Austin, Texas
Austin, Texas has unique water needs shaped by its environment and lifestyle. Choosing between a bladder tank and a pressure tank depends on local conditions. Both tank types serve well but vary in performance based on climate, water quality, and installation practices.
Climate Impact
Austin experiences hot summers and mild winters. The heat can affect tank materials and water pressure. Bladder tanks handle temperature changes better by preventing air loss. Pressure tanks may need more frequent maintenance in this climate. A reliable tank must withstand heat without losing efficiency.
Water Quality Factors
Austin’s water has minerals and occasional sediments. Bladder tanks keep water separate from air, reducing corrosion risks. Pressure tanks expose water to air, which can cause rust over time. For well water users, bladder tanks often provide cleaner, longer-lasting service. Consider water hardness and cleanliness when selecting a tank.
Local Installation Trends
Many Austin plumbers prefer bladder tanks for their low maintenance. Bladder tanks are easier to install in tight spaces common in Austin homes. Pressure tanks remain popular for older systems and larger homes. Local codes and installer experience influence tank choices. Check with local experts to match your home’s needs.
Pros And Cons
Choosing between a bladder tank and a pressure tank involves understanding their pros and cons. Each type offers unique benefits and some potential challenges. This section highlights the advantages and drawbacks of both tanks to help you decide which fits your needs.
Advantages Of Bladder Tanks
Bladder tanks have a flexible rubber bladder inside. This design keeps water and air separate. It prevents waterlogging and maintains consistent pressure. These tanks reduce pump cycling, which extends pump life. They are also low maintenance because the bladder is sealed. The tank adjusts quickly to pressure changes for smooth water flow.
Advantages Of Pressure Tanks
Pressure tanks use an air chamber to maintain pressure. They are usually less expensive upfront than bladder tanks. Their simple design makes them easy to install. These tanks are durable and work well in many systems. They do not have a bladder to wear out or rupture. Some models allow easy air pressure adjustments.
Potential Drawbacks
Bladder tanks can fail if the bladder leaks or bursts. Air may escape, causing the bladder to over-expand. This leads to premature bladder damage and more pump cycling. Pressure tanks can develop waterlogging if the air charge is lost. They require regular checks to maintain proper air pressure. Both tanks need some care to avoid system issues.
Credit: libertysupply.com
Troubleshooting Tips
Troubleshooting bladder tanks and pressure tanks helps keep your water system working well. Both tanks can face issues that reduce performance. Knowing how to find and fix these problems saves time and money. This guide gives simple tips to spot common issues, handle air loss, and take steps to avoid future troubles.
Identifying Common Problems
Check for water leaks around the tank and pipes. Listen for strange noises when the pump runs. Watch for rapid pump cycling, which means the tank is not holding pressure. Low water pressure or no water flow can also signal tank problems. Look at the tank’s pressure gauge to see if it reads too high or too low.
Air Loss Issues
Air loss causes the tank to lose pressure and work poorly. Bladder tanks may lose air if the bladder is damaged or worn out. Pressure tanks lose air if the air valve leaks or the tank becomes waterlogged. A simple test is to press the tank’s side; it should feel firm. If it feels heavy or full of water, air loss is likely the cause.
Preventive Measures
Check the air pressure regularly using a tire gauge. Adjust it to match the pump’s cut-in pressure minus 2 psi. Drain the tank once a year to remove sediment and check the bladder’s condition. Inspect valves and fittings for leaks or damage. Avoid letting the tank freeze by insulating it in cold weather.
Choosing The Right Tank
Choosing the right tank for your water system is vital for efficiency and durability. The decision between a bladder tank and a pressure tank depends on various factors. Understanding these factors helps select the best option for your household. This section breaks down the key points to consider.
Assessing Household Needs
Start by evaluating your water usage. Consider the number of people in your home and daily water demands. High water use may require a larger tank or one with better pressure control. Think about the size of your plumbing system as well. This ensures the tank matches your water flow and pressure needs.
Matching Tank Type To Usage
Bladder tanks have a flexible bladder that holds water, reducing air contact. This design helps maintain steady pressure and reduces pump cycling. Pressure tanks use air chambers and may need regular air checks. For households wanting low maintenance, bladder tanks are a good fit. Pressure tanks work well for simpler systems or where cost is a concern.
Expert Recommendations
Experts suggest bladder tanks for homes with frequent water use. They extend pump life by reducing on-off cycles. Pressure tanks suit smaller homes or setups with less water demand. Regular maintenance is key for pressure tanks to avoid air loss. Consult a professional to assess your system before deciding. Proper installation ensures the tank performs well and lasts longer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Difference Between A Bladder Tank And A Pressure Tank?
A bladder tank has a flexible rubber bladder that separates water and air, preventing corrosion. A pressure tank uses an air chamber without a bladder and may require more maintenance. Bladder tanks reduce pump cycling, while pressure tanks can rust and need regular inspection.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Bladder Tanks?
Bladder tanks can lose air, causing bladder over-expansion and premature failure. This leads to frequent pump cycling and shortens pump life.
Which Is Better, A Diaphragm Or A Bladder Pressure Tank?
Bladder tanks offer better durability and prevent corrosion with a flexible rubber barrier. Diaphragm tanks may require more maintenance and have metal parts prone to rust. Bladder tanks reduce pump cycling, improving performance and lifespan. Overall, bladder tanks typically perform better and need less upkeep.
Do You Need A Bladder Tank For A Well?
A bladder tank is essential for a well to maintain consistent water pressure and reduce pump cycling. It prevents pressure fluctuations and protects the pump, ensuring steady water flow during peak usage. Without it, water pressure may drop and the pump may wear out faster.
What Is The Main Difference Between Bladder And Pressure Tanks?
Bladder tanks have a flexible bladder inside, while pressure tanks use air chambers or diaphragms.
Conclusion
Choosing between a bladder tank and a pressure tank depends on your needs. Bladder tanks offer low maintenance and consistent pressure. Pressure tanks may require more care but can be cost-effective. Both help protect your pump and maintain steady water flow.
Understanding their differences helps you make the right choice. Consider factors like durability, maintenance, and budget. This ensures your water system works smoothly and lasts longer. Keep your home’s water pressure stable and reliable. Simple steps lead to better water performance every day.
