When it comes to your home’s plumbing system, understanding the difference between a vent stack and a stack vent can save you from costly repairs and frustrating issues. You might be wondering—are these just plumbing terms, or do they actually affect how your drains work?
The truth is, knowing how each functions helps you keep your pipes flowing smoothly and your home free from sewer gas odors. You’ll discover exactly what sets a vent stack apart from a stack vent, why each matters, and how they work together to protect your plumbing system.
By the end, you’ll feel confident identifying these important parts and maintaining your home’s drainage like a pro. Ready to clear the air on vent stacks versus stack vents? Let’s dive in.

Credit: up.codes
Basic Plumbing Vent Types
Understanding basic plumbing vent types helps keep your home’s drainage working well. Plumbing vents let air enter the pipes. This air balances pressure and stops sewer gases from entering your home. Two common types are the vent stack and the stack vent. Each plays a unique role in plumbing systems.
Both vents work together to ensure smooth water flow and proper ventilation. Knowing the difference can help with repairs or upgrades. Below, we explain what a vent stack and stack vent are.
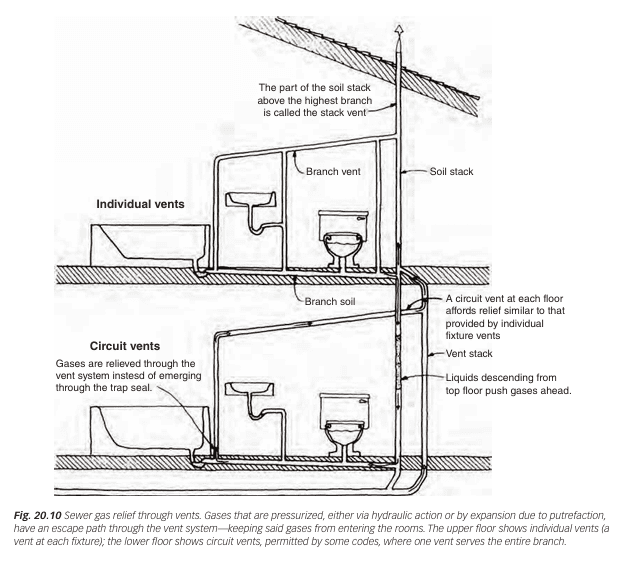
What Is A Vent Stack
A vent stack is a vertical pipe that goes through your roof. It allows sewer gases to escape safely outside. No water flows through this pipe. It connects with the main drain stack inside the house. The vent stack also brings fresh air into the plumbing system.
This air prevents pressure build-up and helps drains work faster. The vent stack is often the tallest pipe on the roof. It is essential for keeping your home free from bad odors and pipe blockages.
What Is A Stack Vent
A stack vent is part of the main waste stack pipe. It extends above the highest fixture in the plumbing system. This vent allows air to enter the stack pipe. It balances pressure inside the waste stack during drainage.
The stack vent is usually inside the building and connects to the vent stack on the roof. It helps prevent water traps from being sucked dry. This keeps sewer gases from entering your home through drains.

Credit: are5community.ncarb.org
Design And Structure Differences
Understanding the design and structure differences between a vent stack and a stack vent helps clarify their roles in plumbing. Both parts serve to vent gases and maintain pressure, but their construction varies significantly. This difference impacts how each functions within the plumbing system.
Vent Stack Construction
A vent stack is a vertical pipe that runs through a building from the drain system to the roof. It carries sewer gases safely outside. The vent stack does not carry water or waste. It is usually made of PVC, cast iron, or ABS materials. The pipe must be sealed and extend above the roofline to allow gases to escape freely.
The vent stack connects to multiple branch vents. These branch vents serve fixtures like sinks, toilets, and showers. Proper vent stack placement ensures balanced air pressure and prevents water traps from drying out. It is a critical part of the overall plumbing ventilation system.
Stack Vent Construction
A stack vent is a continuation of the main waste stack that extends above the highest horizontal drain connection. Unlike the vent stack, the stack vent carries both waste water and air. It starts where the main waste stack ends and rises through the roof to vent gases.
Stack vents are built to handle both drainage and venting functions. They must be sized correctly to handle the flow of waste water and air pressure. These vents usually have a larger diameter near the bottom and taper as they rise. This design helps maintain flow and venting efficiency.
Functional Roles In Plumbing
Understanding the functional roles in plumbing helps clarify the difference between vent stack and stack vent. Both parts are vital for safe and efficient plumbing systems. They manage air pressure and allow sewer gases to escape. This keeps water flowing smoothly and prevents odors inside the building.
Purpose Of A Vent Stack
A vent stack is a vertical pipe that runs through the roof. It allows sewer gases to exit the plumbing system safely. No water flows through this pipe. It also helps balance air pressure inside the drain pipes. This prevents water traps from being sucked dry. Without a vent stack, drains can gurgle or drain slowly.
Purpose Of A Stack Vent
A stack vent is the upper part of the main waste stack. It extends above the highest drain connection and opens through the roof. Its job is to vent air from the waste stack itself. This stops pressure build-up inside the stack. The stack vent supports proper drainage from all connected fixtures. It ensures waste moves down without blockage or backflow.
Placement And Location
Understanding the placement and location of vent stacks and stack vents is crucial for proper plumbing function. These components help maintain air pressure in pipes and allow sewer gases to escape safely. Their position affects how well your plumbing system works and prevents issues like slow drainage or bad odors.
Where Vent Stacks Are Used
Vent stacks are installed vertically through the roof of a building. They connect to the main drain pipes and extend above the roofline. This placement allows sewer gases to exit outside the home safely. Vent stacks serve multiple fixtures by connecting to the main waste stack. They are common in larger plumbing systems with several bathrooms or kitchens. The vertical location ensures proper air flow and pressure balance in the system.
Where Stack Vents Are Installed
Stack vents are part of the main waste stack but only extend above the highest fixture drain. They are located inside the building and do not always go through the roof. Stack vents provide ventilation for a specific drain stack. These vents prevent traps from losing water seal by allowing air into the system. Stack vents are often used in simpler or smaller plumbing setups. Their placement depends on the height of the highest fixture connected to the stack.
Applications By Building Size
Understanding the applications of vent stacks and stack vents depends largely on building size. Different plumbing needs arise from smaller homes compared to larger or multi-story buildings. These differences influence the choice between a vent stack and a stack vent. Each system serves to maintain air pressure and allow gases to escape, but their use varies with building scale and complexity.
Use In Smaller Homes
In smaller homes, vent stacks are often preferred. They provide a simple and effective way to vent plumbing fixtures. A vent stack runs vertically through the roof, allowing air into the drainage system. This prevents suction that can block water flow or trap sewer gases inside. Since smaller homes have fewer plumbing fixtures, a single vent stack usually meets all venting needs. Installation is straightforward and cost-effective. This system ensures proper drainage and safe air pressure levels in the pipes.
Use In Larger Or Multi-story Buildings
Larger or multi-story buildings require more complex venting solutions. Stack vents are more common in these structures. A stack vent is the upper part of a waste stack that extends above the highest fixture branch. It vents multiple floors through one vertical pipe. This design helps balance air pressure across many plumbing fixtures on different levels. It reduces the number of individual vent pipes needed. Stack vents are essential for maintaining proper drainage and preventing sewer gas buildup in tall buildings. They also help meet plumbing codes that regulate multi-story construction.
Advantages And Limitations
Understanding the advantages and limitations of vent stacks and stack vents helps in choosing the right plumbing system. Both serve important roles in venting air and gases from drains. Each has benefits and some challenges that affect installation and performance.
Benefits Of Vent Stacks
Vent stacks provide direct air flow from the plumbing system to the outside. This helps balance pressure and prevent sewer gases from entering the home. They are simple to install and maintain. Vent stacks reduce the risk of drain traps being emptied by negative pressure. They support multiple fixtures and ensure smooth drainage. Their vertical design fits well in most building layouts. Vent stacks also improve air circulation within the plumbing system, reducing blockages.
Challenges With Stack Vents
Stack vents can be more complex to install due to their location on the main waste stack. They require careful planning to avoid blockages and maintain proper airflow. Stack vents may be less effective if the vent pipe is too long or has sharp bends. They might need more roof space for proper venting. In cold climates, stack vents can allow cold air to enter, which may cause pipe freezing. Regular inspection is necessary to avoid vent clogs and maintain system health.
Code Requirements And Standards
Understanding the code requirements and standards for vent stacks and stack vents is essential for safe plumbing. These codes ensure proper air flow, prevent sewer gases from entering buildings, and maintain system pressure. Compliance with local and national guidelines protects both property and health.
Building inspectors rely on these codes to verify installations meet safety and functionality criteria. Builders and plumbers follow them to avoid costly repairs and legal issues. The codes also help maintain consistent performance across different structures.
Building Code Guidelines For Vent Stacks
Vent stacks must comply with the International Plumbing Code (IPC) or local building codes. They require vent stacks to extend through the roof to release sewer gases safely. The height and diameter are set to ensure adequate air flow and prevent blockages.
Codes specify materials that resist corrosion and maintain structural integrity. Vent stacks should be installed vertically without sharp bends to allow smooth gas flow. Proper clearance from windows and air intakes is mandatory to avoid contamination.
Regulations For Stack Vents
Stack vents are regulated to connect properly with the main waste stack. They must rise at least 6 inches above the flood-level rim of the highest fixture served. This prevents water from entering the vent and causing blockages.
Local codes often require stack vents to be sized according to the number of fixture units they serve. Materials must meet fire-resistance and durability standards. Installation rules ensure vents do not interfere with structural elements or other utilities.
Common Issues And Maintenance
Understanding common issues and maintenance for vent stacks and stack vents helps keep plumbing systems working well. These vents play a key role in releasing sewer gases and balancing air pressure in pipes. Ignoring problems can cause bad smells, slow drains, or pipe damage. Regular checks and simple care prevent costly repairs.
Problems With Vent Stacks
Vent stacks often face blockages from leaves, debris, or bird nests. These clogs stop air flow and cause pressure issues in pipes. Cracks or leaks in vent stacks allow sewer gases to enter the home, creating health risks. Ice buildup in cold weather can also block vents and damage pipes. Poor installation may lead to improper venting and drainage problems.
Stack Vent Maintenance Tips
Clear debris from vent openings regularly to avoid blockages. Inspect vent stacks for cracks or damage twice a year. Use a plumber’s snake or air jet to remove stubborn clogs inside vents. Make sure vent caps are secure and free of nests or dirt. During winter, check vents for ice buildup and remove it carefully. Hire a professional plumber for thorough inspections and repairs when needed.
Impact On Home Safety And Comfort
Understanding the impact of vent stacks and stack vents on home safety and comfort is crucial. These plumbing components play key roles in protecting your home from harmful gases and ensuring smooth drainage. The right vent system helps keep your indoor air clean and your plumbing working efficiently. Let’s explore how they affect sewer gas prevention and air pressure balance inside your home.
Preventing Sewer Gas Entry
Vent stacks and stack vents stop sewer gases from entering living spaces. Sewer gases can cause bad odors and health risks. Proper venting allows these gases to escape safely outside. A vent stack runs vertically through the roof, providing a path for gases to leave. Stack vents, connected to waste stacks, also help release gases above the roofline. Both reduce the chance of gas buildup indoors, keeping your home safer.
Maintaining Proper Air Pressure
Air pressure in plumbing pipes must stay balanced for drains to work well. Vent stacks let air flow into pipes, preventing vacuum conditions. Without this air, water traps can be sucked dry, allowing sewer gases in. Stack vents provide similar airflow along the main drain lines. Balanced air pressure helps water flow smoothly and stops gurgling sounds in drains. This balance improves home comfort by preventing odors and plumbing issues.
Credit: academy2.youngarchitect.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Code For Vent Stacks?
The code for vent stacks follows the International Plumbing Code (IPC). It requires vent stacks to extend through the roof, maintaining proper air circulation and preventing sewer gases indoors. Vent stacks must meet size, height, and material standards to ensure safe, efficient plumbing venting.
What Is A Main Vent Stack?
A main vent stack is a vertical pipe extending through the roof. It vents sewer gases and balances air pressure in plumbing. No water flows through it. It connects fixtures to the outside, ensuring proper drainage and preventing sewer gas buildup inside the home.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Stack Ventilation?
Stack ventilation can cause excessive heat loss in winter and may lead to over-ventilation. It depends on temperature differences and may reduce indoor comfort.
Do You Need A Vent Stack?
A vent stack is necessary to maintain proper drainage and prevent sewer gases from entering your home. It ensures air circulation in the plumbing system.
What Is The Main Difference Between A Vent Stack And A Stack Vent?
A vent stack is a vertical pipe for venting sewer gases. A stack vent is the upper part of the waste stack acting as a vent.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between a vent stack and a stack vent helps with plumbing clarity. A vent stack carries air through the roof to balance pressure. A stack vent extends from the highest drain to release gases safely. Both keep drainage systems working well and prevent sewer odors indoors.
Knowing their roles supports better home maintenance and plumbing care. Proper venting ensures pipes drain smoothly and your home stays safe. Simple yet crucial parts of plumbing, these vents play key roles daily.
