Have you ever wondered what makes your gas stove light up and cook your meals so quickly? Understanding how a gas stove works can help you use it more safely and efficiently.
Whether you’re curious about the flame you see or want to know how it can still work during a power outage, this guide is made just for you. By the end, you’ll discover simple tips to light your stove manually and learn why some parts of your stove need electricity while others don’t.
Keep reading to unlock the secrets behind your gas stove and take control of your kitchen like a pro!
Gas Stove Basics
A gas stove uses natural gas or propane to create heat for cooking. It provides instant heat and easy temperature control. The flame heats pots and pans directly, making cooking efficient and fast.
Understanding the basic parts helps explain how gas stoves work. Each part plays a role in safely delivering and igniting gas to cook food.
Key Components
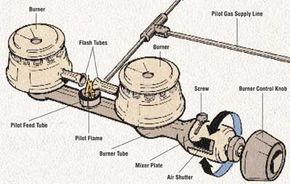
The main parts of a gas stove include burners, gas valves, and ignition systems. Burners are where the flame appears to heat cookware. Gas valves control the flow of gas to the burners. Ignition systems light the gas to start the flame.
Burners have small holes to release gas evenly for a consistent flame. The control knobs adjust the gas valve to change flame size and heat level. Some stoves use electronic ignition to spark the flame, while others require manual lighting.
Fuel Source
Gas stoves run on natural gas or propane, depending on the home setup. Natural gas comes through a pipeline and is common in cities. Propane is stored in tanks and used in areas without gas lines.
The fuel flows from the source to the stove through pipes or hoses. The stove regulates the gas flow to maintain the flame. Proper fuel supply ensures safe and steady cooking heat.
Credit: home.howstuffworks.com
Ignition Methods
Gas stoves use different ignition methods to light the burners. These methods control how the gas ignites safely and quickly. Understanding ignition methods helps users operate the stove efficiently and safely. Three common types include electronic ignition, manual lighting, and standing pilot light.
Electronic Ignition
Electronic ignition uses a small electric spark to light the gas. When you turn the knob, the stove creates a spark near the burner. This spark ignites the gas immediately. It is fast and convenient. Many modern gas stoves use this method. It saves energy because the spark only happens when needed.
Manual Lighting
Manual lighting requires a match or lighter to ignite the gas. This method works without electricity. Users must turn the gas knob and light the burner simultaneously. It is useful during power outages. However, it needs caution to avoid gas buildup. Some stoves may not allow manual lighting for safety reasons.
Standing Pilot Light
A standing pilot light is a small flame that stays lit continuously. It ignites the gas when you turn the burner on. Older gas stoves often use this method. It consumes some gas even when the stove is off. This method is reliable but less energy efficient than electronic ignition.
How Flame Is Controlled
The flame on a gas stove is carefully controlled to provide the right amount of heat for cooking. This control depends on adjusting the gas flow and managing the burner flames. Proper flame control helps save energy and ensures safe cooking.
Gas Flow Regulation
The gas flow controls the size of the flame. It starts when you turn the stove knob. Inside the stove, a valve opens to let gas pass through. The more you turn the knob, the more gas flows out.
Less gas means a smaller flame. More gas creates a bigger flame. The gas mixes with air before burning, so the flame burns cleanly and steadily. This process keeps the flame stable and easy to adjust.
Adjusting Burner Flames
After the gas flows, the flame size can be changed by turning the control knob. This adjustment changes the gas amount reaching the burner. A low flame saves fuel and is good for simmering.
A higher flame heats food faster and is used for boiling or frying. The flame should be blue with small tips. Yellow or flickering flames mean poor gas or air mix and need fixing.
Cooking With A Gas Stove
Cooking with a gas stove offers many benefits that make it a popular choice in kitchens. The instant flame provides immediate heat, allowing quick cooking. Gas stoves give great control over the cooking process, which helps prepare food evenly and efficiently.
Heat Distribution
Gas stoves distribute heat directly to the cookware. The flame touches the bottom of the pan, spreading warmth evenly. This helps avoid hot spots and burns. Heat moves quickly, so food cooks faster than with electric stoves. Even heat distribution improves the taste and texture of meals.
Temperature Control
Gas stoves allow precise temperature adjustments. Turning the knob changes the flame size immediately. Small flames mean low heat for simmering sauces. Large flames provide high heat for boiling or frying. This quick response helps cook food perfectly without overcooking or burning.
Power Outage Effects
Power outages can affect gas stoves in several ways. While gas stoves mainly use gas for cooking, many parts rely on electricity. Knowing what works and what does not helps in managing cooking during a blackout. Some functions continue, but others stop completely.
Burner Operation Without Electricity
Gas stove burners can work without electricity. You must light them manually with a match or lighter. This bypasses the electric ignition system. Turn the burner knob slowly to release gas. The flame will light from the match. Not all stoves allow manual lighting. Check your stove’s manual before trying.
Oven Functionality
The oven usually needs electricity to work. It uses an electric ignition to light the gas. During a power outage, the oven will not turn on. The gas valve will not open without power. The oven light also will not work. Cooking with the oven is not possible until power returns.
Control Panel Limitations
Electric control panels stop working during outages. Timers, clocks, and digital displays turn off. You cannot use electronic cooking modes. The control panel will not respond to commands. Cooking settings must be adjusted manually if possible. This limits the stove’s full functionality until power comes back.
Safety Tips
Using a gas stove requires attention to safety. Gas leaks and improper use can cause accidents. Follow these safety tips to keep your kitchen safe and your cooking efficient.
Proper Ventilation
Always ensure your kitchen has good airflow. Open windows or use an exhaust fan. This helps remove gas fumes and prevents buildup. Proper ventilation reduces the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning. Never use a gas stove in a closed room for a long time.
Manual Lighting Precautions
Only light burners manually if your stove allows it. Keep matches or lighters ready before turning the gas on. Turn the knob slowly to avoid gas buildup. Light the burner immediately after turning the gas. Never leave the gas on without lighting it. This prevents dangerous gas leaks and fires.
Model-specific Features
Check your stove’s manual for special safety features. Some models have automatic shut-off systems. Others may block manual lighting for safety. Know how your stove works to avoid accidents. Follow manufacturer instructions for safe use and maintenance.
Modern Vs Older Stoves
Gas stoves have evolved over time, changing how they ignite and operate. Older models often use simple methods, while modern ones use advanced technology. This section compares the two types to help you understand their differences.
Electronic Ignition Systems
Modern gas stoves mostly use electronic ignition systems. These systems create a small electric spark to light the burner instantly. They save energy because the flame only lights when needed. This system is safer and more reliable than older methods. It also reduces gas waste by preventing gas from flowing before ignition.
Electronic ignition needs electricity to work. During power outages, some stoves may not light automatically. Many modern stoves include a backup manual lighting option for such cases. This system is quieter and cleaner since it does not use a constantly burning flame.
Standing Pilot Light Systems
Older gas stoves usually have a standing pilot light system. This system keeps a small flame burning all the time. The pilot light ignites the burner when you turn the knob. It does not need electricity, so it works during power cuts.
Standing pilot lights waste more gas because they burn continuously. They can also be less safe, as the flame may go out, causing gas to leak. Older stoves with pilot lights require more maintenance to keep the flame steady and clean.

Credit: woolfplumbing.com.au
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does A Gas Stove Work Without Electricity?
A gas stove works without electricity by manually lighting burners with a match or lighter, bypassing electronic ignition. Only stovetop burners work; ovens and digital features need power. Always follow safety guidelines and check your stove’s manual for manual lighting instructions.
Should I Open A Window When Using A Gas Stove?
Yes, open a window when using a gas stove to ensure proper ventilation and reduce harmful gas buildup.
Is It Healthier To Cook With Gas Or Electric?
Cooking with gas offers better temperature control but can emit indoor pollutants. Electric cooking is cleaner and safer indoors. For health, electric cooking generally ranks higher due to reduced indoor air pollution.
Where Does The Gas Come Out On A Gas Stove?
Gas exits through small holes around the burner rings on a gas stove. These holes release gas to ignite flames for cooking.
How Does A Gas Stove Ignite The Burner?
Gas stoves ignite by releasing gas that mixes with air and is sparked to produce a flame.
Conclusion
Understanding how a gas stove works helps you use it safely and efficiently. Gas flows through pipes to the burner, where it mixes with air and ignites. You can light burners manually during power outages by using a match or lighter.
Remember, ovens and electric features need power to work. Always follow safety steps and check your stove’s manual. This knowledge ensures you cook with confidence, whether the power is on or off.
