When it comes to wiring outlets in your home, understanding the difference between series and parallel setups can save you time, money, and frustration. You might wonder why outlets are almost always wired in parallel rather than in series—and what impact that choice has on your power supply and safety.
If you’re planning to do some electrical work yourself or simply want to know how your home’s outlets function, this article will clear up the confusion. By the end, you’ll know exactly why parallel wiring is the standard, how series wiring affects your outlets, and which method is right for your needs.
Keep reading to make smarter, safer decisions for your home’s electrical system!
Series Wiring Basics
Series wiring connects outlets one after another on a single path. Electricity flows through each outlet in turn. This setup creates a chain where all outlets share the same current.
Understanding series wiring is important for basic electrical projects. It shows how voltage and current behave in a simple circuit. This knowledge helps in deciding when to use series wiring.
Circuit Path Setup
In series wiring, outlets connect end-to-end. The current flows from the power source through each outlet. There is only one path for the electricity to travel.
If one outlet or device stops working, the entire circuit breaks. This means all other outlets lose power. The flow depends on every connection being complete.
Voltage Distribution
The voltage divides across each outlet in a series circuit. Each outlet drops some voltage based on its resistance. The sum of all drops equals the total voltage from the source.
Outlets farther from the power source get less voltage. This can cause devices to work poorly or not at all. Voltage decreases as electricity moves along the circuit.
Common Applications
Series wiring is used in simple devices like string lights. It helps control multiple bulbs with one switch. This setup is easy to install for low-power needs.
Series circuits are less common for home outlets. They are not safe for general use because one failure affects all devices. Parallel wiring is better for reliable power in homes.
Parallel Wiring Basics
Parallel wiring is the standard method for connecting electrical outlets in homes. This setup allows each outlet to operate independently. It ensures that power remains available even if one outlet stops working. Understanding the basics of parallel wiring helps in safe and effective electrical installations.
Circuit Path Setup
In parallel wiring, each outlet connects directly to the power source. This creates multiple paths for electricity to flow. Each outlet gets its own connection line from the circuit. This setup prevents one outlet from affecting another.
Voltage Consistency
Each outlet in a parallel circuit receives the same voltage. This means devices plugged into any outlet get full power. Voltage does not drop as more outlets are added. This consistency keeps devices running properly without power loss.
Common Applications
Parallel wiring is used in almost all home electrical outlets. It powers lamps, appliances, and electronic devices safely. This wiring style also applies to lighting circuits and kitchen outlets. It supports multiple devices without interruption or power issues.
Key Differences Between Series And Parallel
Parallel wiring is the best choice for electrical outlets in homes and buildings. It provides a safer and more reliable power supply. Each outlet gets its own direct connection to the power source. This design improves performance and convenience for everyday use.
Consistent Power Supply
Parallel wiring delivers equal voltage to every outlet. Each outlet works at full power, regardless of others. This prevents dimming or power drops when multiple devices run simultaneously. The steady voltage ensures devices perform correctly and safely.
Independent Outlet Operation
Outlets in parallel work independently of each other. If one outlet or device fails, others keep working normally. This avoids total power loss in a room or area. Users can safely plug and unplug devices without affecting the entire circuit.
Compliance With Electrical Codes
Electrical codes require outlets to be wired in parallel. This standard protects users and property from electrical hazards. Parallel wiring meets safety rules and inspection requirements. It ensures the electrical system is legal and reliable for daily use.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Series-and-parallel-circuits-the-basics-1152850-055e134b2b5847a5ae5b28843bbc3c39.png)
Credit: www.thespruce.com
Why Parallel Wiring Is Preferred For Outlets
Wiring outlets in series carries several risks that affect performance and safety. This setup is uncommon in homes due to its many drawbacks. Understanding these risks helps avoid electrical problems.
Series wiring connects outlets one after another on a single path. This design causes issues that do not happen with parallel wiring.
Voltage Drop Issues
Voltage decreases as electricity passes through each outlet in series. Outlets farther from the source get less power. Devices may not work properly or may run slower. This problem worsens with more outlets on the line.
Circuit Interruptions
If one outlet or device fails, the entire circuit stops working. A loose connection or broken device cuts power to all outlets. Troubleshooting becomes harder because one fault affects many outlets. This leads to frequent outages and frustration.
Safety Concerns
Series wiring increases the risk of overheating due to current flow through multiple devices. Overheated wires can cause fires. It also complicates grounding and protection measures. Poor safety increases hazards for people and property.
Risks Of Wiring Outlets In Series
Understanding the legal and code considerations for wiring outlets in series versus parallel is crucial. Electrical work must follow strict rules to ensure safety and proper function. Ignoring these rules can lead to hazards like electrical fires or shocks. This section covers important codes and guidelines to help you comply with the law and keep your home safe.
National Electrical Code Guidelines
The National Electrical Code (NEC) sets the standard for safe electrical installations in the U.S. It requires outlets to be wired in parallel circuits, not series. Parallel wiring ensures each outlet receives full voltage independently. This prevents one outlet failure from shutting off the entire circuit.
The NEC also specifies outlet spacing, grounding, and wiring methods. Outlets must be installed at certain intervals to avoid long gaps without power. Proper grounding protects against electrical shocks. Following these rules reduces risks and meets legal standards.
Local Regulations In Austin, Texas
Austin has additional electrical codes building on NEC rules. Local laws may set stricter requirements for outlet placement and types. Permits are often required before starting any electrical work. These rules ensure that installations suit the local climate and building styles.
Electricians in Austin must stay updated on city amendments to the NEC. Inspections by city officials confirm that all wiring meets local codes. Homeowners should check with the Austin Electrical Inspection Department before beginning projects.
Inspection And Compliance Tips
Arrange inspections early and keep records of all permits. Inspectors check outlet wiring, grounding, and overall safety. Correct any issues they find to pass the inspection.
Use licensed electricians familiar with NEC and Austin codes. Test all outlets after wiring to ensure proper operation. Document your work with photos and notes. This helps prove compliance and makes future repairs easier.
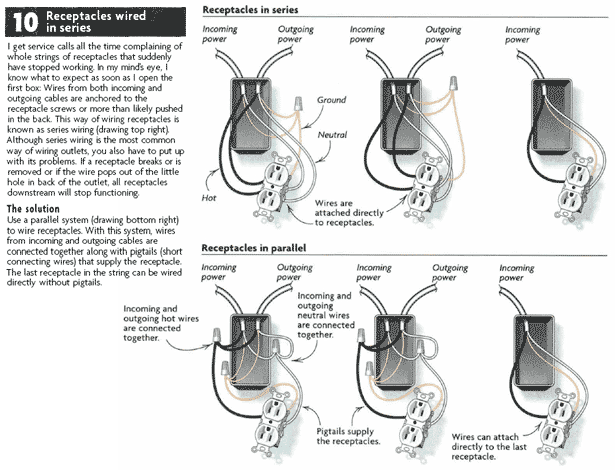
Credit: www.finehomebuilding.com
Techniques For Parallel Wiring
Choosing the right wiring method for outlets depends on the specific needs of your project. Some situations require careful thought about whether to wire in series or parallel. The choice impacts voltage, current flow, and device performance.
Understanding these factors helps prevent issues like power loss or device failure. Below are key special cases to consider when selecting between series and parallel wiring.
High Voltage Requirements
Series wiring increases total voltage across devices. Each outlet receives a portion of the total voltage. This suits setups needing higher voltages than a single outlet can provide. However, if one outlet fails, the entire circuit stops working.
Parallel wiring keeps voltage consistent across outlets. Each outlet gets the full voltage supplied by the source. This is safer for typical household devices that need steady voltage. It avoids voltage drops seen in series wiring.
Power Appliance Considerations
Powerful appliances require stable voltage and current. Parallel wiring ensures each appliance receives full voltage and sufficient current. Series wiring can cause voltage drops, making appliances underperform or fail.
Using parallel wiring reduces risk of damage to sensitive or high-power devices. It also allows independent operation, so one appliance’s failure does not affect others.
Battery Wiring Comparisons
In battery setups, series wiring raises voltage by adding battery voltages. This suits devices needing higher voltage but same current. Parallel wiring keeps voltage the same but increases available current.
Choosing series or parallel in batteries depends on required voltage and current. Series suits high voltage, low current needs. Parallel fits low voltage, high current applications. Both methods affect battery life and device function.
Legal And Code Considerations
Troubleshooting wiring issues in outlets requires careful inspection and clear understanding. Series and parallel wiring have different symptoms when problems occur. Identifying these problems quickly helps avoid extended downtime and safety risks.
Many common problems involve power loss, flickering, or devices not working. Knowing how to spot these issues and fix them improves outlet performance. This section covers key ways to troubleshoot wiring issues effectively.
Identifying Series Wiring Problems
In series wiring, all outlets share one path. If one outlet fails, others lose power too. This is a clear sign of series wiring issues. Check if a single outlet outage affects others downstream.
Look for dim lights or devices that stop working suddenly. Loose connections in the chain cause these problems. Inspect each outlet connection carefully to find the faulty link.
Fixing Voltage Drops
Voltage drops occur when wiring is too long or connections are weak. This causes devices to run poorly or not at all. Use a voltmeter to measure voltage at each outlet.
If voltage is low, tighten all wire connections. Replace damaged wires or use thicker wire to reduce resistance. Proper wiring in parallel minimizes voltage drops and keeps outlets working well.
Ensuring Outlet Reliability
Reliable outlets maintain steady power and respond well to devices. Avoid wiring outlets in series for home circuits. Parallel wiring provides stable voltage to each outlet.
Test outlets regularly with a socket tester. Replace worn or damaged outlets immediately. Secure wires and use proper connectors to prevent loose contacts. This keeps your electrical system safe and dependable.
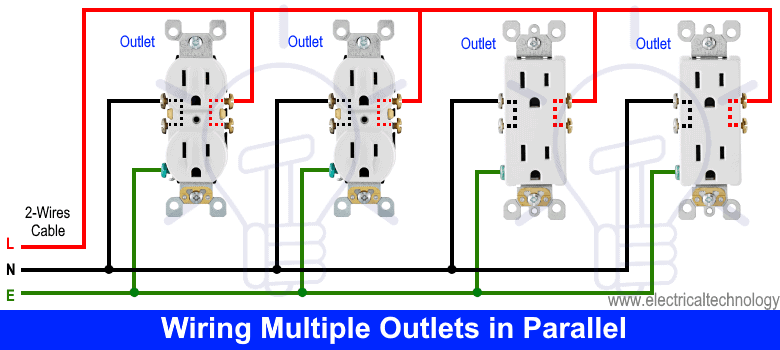
Credit: diy.stackexchange.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The 2 6 12 Rule For Outlets?
The 2-6-12 rule requires placing outlets within 2 feet of corners, every 6 feet along walls, and no more than 12 feet apart. This ensures convenient access and meets electrical code standards.
Why Are Outlets In Homes Never Wired In Series?
Outlets in homes are never wired in series because a failure in one breaks the entire circuit. Series wiring causes voltage drops, reducing power to outlets. Parallel wiring ensures each outlet receives full voltage and works independently, providing safer and more reliable power distribution.
When To Use Series Vs Parallel?
Use series circuits to increase voltage for high-power devices. Choose parallel circuits to maintain constant voltage and independent operation for outlets. Parallel wiring ensures one device’s failure doesn’t affect others, making it ideal for home electrical outlets and consistent power delivery.
Is It Legal To Wire Outlets In Series?
Wiring outlets in series is generally not legal or safe. Outlets must be wired in parallel to ensure consistent voltage and avoid circuit failure. Parallel wiring keeps each outlet powered independently, meeting electrical codes and safety standards. Always follow local electrical regulations when wiring outlets.
What Is The Difference Between Series And Parallel Wiring?
Series wiring connects outlets one after another, while parallel wiring connects each outlet directly to the power source.
Conclusion
Wiring outlets in parallel keeps power steady and safe. Each outlet works independently without affecting others. Series wiring can cause all outlets to fail if one stops working. Parallel setups make it easier to add or fix outlets later. Always choose parallel wiring for home safety and convenience.
Understanding these basics helps you plan your electrical system well. Safe wiring protects your home and devices. Keep your circuits simple, reliable, and easy to maintain.
